-
[기계학습] 13. Class Imbalanced Problems🐳Dev/Machine Learning 2021. 12. 9. 17:09
오늘은 데이터 불균형의 문제와 해결방법에 대해 이야기 해보려고 한다.
알고리즘을 공부할 때는 우리가 추출하려는 데이터와 일반적인 데이터가 대략 1 : 1의 비를 가진다고 가정한다.
하지만 실제 상황에서는 이 두 데이터간의 비의 차이가 비슷한 경우는 거의 없다.
1. Class-Imbalanced Problems
분류하는 상황에서, 우리가 추출하려는 데이터는 positive, 일반적인 데이터는 negative이라고 부른다.
In classification problems,
- The total number of a class of data (positive) is far less than the total number of another class of data (negative)
- The minority class is a rare event or the data in minority class is hard to collect
- Example – Majority class : Minority class = 9:1
- Problem – A classifier tends to classify all data to the majority class
그리고 일반적으로 추출하려는 데이터는 양이 매우 적다. 예를 들어 Fault Detection, Cancer detection 등을 생각하면, 우리가 찾고자하는 데이터는 일반적이지 않고 특수하다.
- What may cause the class-imbalanced problems
- It is hard to collect the minority data
- Minority data are collected from rare events
- Minority class is often what we are interested in
- Minority class: positive
- Majority class: negative
- We are interested in prediction of the minority class
- In real-world cases, we barely deal with problems at 50:50
1) Class-Imbalanced Problems
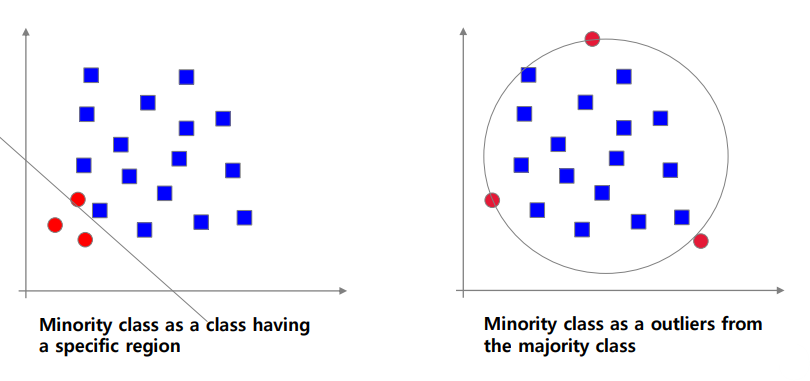
- Two perspectives on class-imbalanced problems
minority class를 일반적으로 두가지 분포로 나눌 수 있다
왼쪽은 minority가 영역을 이루고, 정의가 가능하다
오른쪽은 영역을 이루지 않고, major가 아닌 경우 minor로 취급한다

- Possible classification results from the conventional 2-class classifiers
이러한 상황에서 decision boundary를 설정하면 다음과 같다
- Desired classification results
하지만 iid에 의해 여러 데이터가 존재할 수 있으므로,
우리는 거리가 유지되는, 적절한 decision boundary를 필요로 한다
아래 예시는 majority와 minority의 비에 따른 decision boundary이다.
비의 차이가 커질 수록 minoiry가 무시되는 것을 볼 수 있다.

2. Sampling Method
따라서 sampling technique를 통해 두 클래스간의 균형을 맞추기로 한다.
가장 간단하고 쉬운 방법은 sampling이다.
- Oversampling, minority를 늘리기
- UnderSampling, majority를 줄이기

1) Oversampling
Oversample from the minority class
- Make duplicates, 같은 값을 복제하거나
- Add random noises, 랜덤 노이즈를 첨가한 데이터를 추가
minority를 늘리기 위해 위와 같은 방식을 사용할 수도 있으며,
주로 사용되는 Oversampling 방법으로는 SMOTE(Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique)가 있다.
꽤 오래된 방법이며, 단점도 존재하지만 여전히 많이 쓰이는 방법이다.
SMOTE
SMOTE는 특정 minority sample k와 k 주변 minoirty data와 선분을 형성하고, 랜덤 비율로 선분 위의 한 지점에 data를 생성하는 방법이다. 데이터들의 내부에만 형성되어 넓고 풍성한 데이터는 생성하기 어려우며, 만약 majority가 중심에 있고 minority가 외각에 있는 모델에서는 의미가 없는 data가 생성될 수 있다는 단점이 있다.

2) Undersampling
Undersample from the majority class
- Random removal, 랜덤으로 제거
- Clustering-based removal, 클러스터에서 핵심 data만 남기고 제거
랜덤으로 제거하는 경우, majority의 특정 영역 data들을 전부 지워 majority를 침범하는 이상한 decision boundsasry를 생성할 수 있다. 따라서 클러스터 기반의 제거를 추천한다.

3. Cost-Sensitive Learning
1) Cost-sensitive learning
Set the cost of misclassification to calibrate ratio between classes
minority data에 대한 오분류에 더 큰 panelty을 부여하는 방식이다- If Positive : Negative = 1:9
- Cost of misclassification –Positive : Negative = 9:1
- Same results from the oversampling without additional noises

식은 간단히 Losss function을 클래스에 따라 다른 가중치를 부여하는 방식으로 구현한다.

Cost-Sensitive Learning을 통해 왼쪽 상황에서는 빨강이를 하나 침범하고 9점의 패널티를 얻었지만, 오른쪽 상황에서는 파랑이를 두 개 넘고도 2점의 패널티를 얻은 것을 볼 수 있다. 그렇다면 모델은 파랑이보다 빨강이를 더 조심할 것이다.
4. Ensemble
- To reduce the variance of sampling methods
앙상블을 majority를 minority와 비슷한 크기로 나누어 여러번 학습시키는 방법이다.

5. Novelty Detection
이 외의 방법에는 Novelty Detection, 이상치 참지가 있는데, 같은 말로는 1-Class Classification, Outlier Detection, Anormaly Detection, Abnormality Detection가 있다.
1) 1 - Class Classification
minority가 없다고 생각하고, majority 하나의 클래스로 학습하고 boundary(정상 범위)를 결정한다. 그리고 이에 해당하지 않는 data는 다른 클래스(이상)라고 판단한다.
맨 처음에 minority를 두 가지 경우로 분류했을 때의 두 번째 경우와 같다.
- Train a model with only data of the majority class
- Define a region of majority class
- Outside the defined region -> minority class
- Like unsupervised method
- Highly imbalanced problems, 매우 불균형할 때 사용
- Positive : Negative = 1 : 999
Binary Classification과 비슷하다고 생각할 수 도 있지만, 이 둘은 철학적 특징이 아에 다르다.

- The number of data belonging to the minority class is too small
- The definition of minority class is just NOT-majority class
Binary에서는 A와 B가 Major이지만, Novelty에서는 아니다. 이 둘이 어떻게 분류되는가가 큰 철학적 특징의 차이 - Generalization vs. specialization

binary는 minorty를 통해 boundary를 조절할 수 있다. 하지만 Novelty는 외부로부터의 영향을 전혀 받지 않으므로 현재의 boundary보다 더 커지는게 좋을지, data와 딱맞게 설정하는 것이 좋은지 결정할 수 없다. 물론 요새는 하이브리드로 적절한 크기의 boundary를 찾을 수 있다.
2) Clustering-based method
클러스터 밖으로 벗어나면 이상치, 안에 있다면 정상을 의미한다
- Clustering with only data belonging to the majority class
- Set a threshold that decides the novelty
- Eg. Distance from each center, bottom p% of training data
노이즈가 있을 수 있으니 클러스터에 margin을 조금 두자!
- Eg. Distance from each center, bottom p% of training data

3) Density estimation-based method
이 또한 범위 내에 있으면 정상치, 밖에 있다면 이상치를 의미한다
- Density estimation with only data belonging to the majority class (eg. GMM 가우시안 혼합 모델)
- Set a threshold that decides the novelty
- Eg. Probability value, bottom p% of training dat

4) Reconstruction-based method
NN을 이용하여 Novelty Detection도 가능하다
차원을 축소하는 과정을 Encode, 다시 확장하는 과정을 Decode라고 하는데 이때 확장을 재구축의 의미로 Reconstruction이라고도 한다. 원본과 새로운 값의 차이를 줄이기 위해 loss를 최소화 하는데, 최대한 의미있는 변수만을 Encode하기에 변수 추출과도 큰 연관이 있다.
다시 돌아와, 원본을 복원해야하는 이 모델은 원본에 집중하여 학습을 하게 된다. 아래의 예시에 따르면 저 모델은 버섯에 집중하여 학습을 하기에, 버섯이 아닌 마리오가 input으로 들어오면 reconsturction error가 매우 커지게 된다.
물론 버섯들로 모델링을 해도 오차는 분명히 존재한다. 따라서 특정 threshold를 넘으면 이상치라고 판단한다.
- Replicator neural networks (autoencoder)
- Train a neural network to minimize the reconstruction error

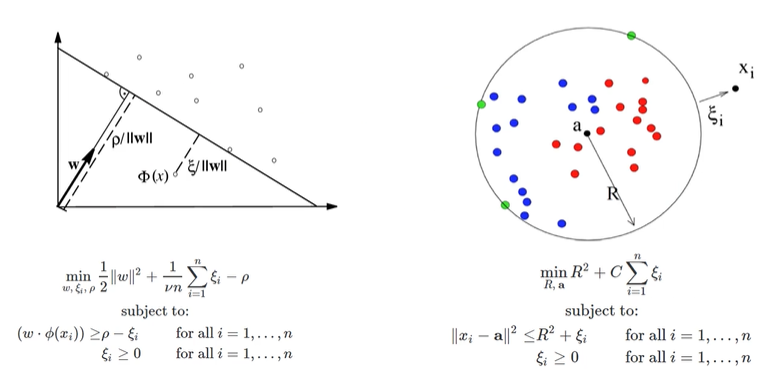
5) Support vector machine-based method
- 1-class SVM (1-SVM) vs. Support vector domain (data) description (SVDD)
6. Summary
- 범주 불균형 문제는 일반적인 2-class 분류기로는 해결하기 어려움
- 해결책
- Sampling, cost-sensitive 등의 보정을 하고 2-class 분류기로 해결
- Novelty detection method 사용, 이상치탐지
마지막으로 ML의 두 가지 명언을 알아보자
Occam's Razor, “If there are various logical ways to explain a certain phenomenon, the simplest is the best”
Wolpert, "No Free Lunch Theorem" : 특정 문제에 최적화된 알고리즘은 다른 문제에는 그렇지 않다
이상으로 머신러닝 수업 끝!
'🐳Dev > Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
[기계학습] 5. Nearest Neighbor Method (0) 2021.12.20 [기계학습] 4. Logistic Regression (0) 2021.12.15 [기계학습] 3. Regression (0) 2021.12.14 [기계학습] 2. Bayesian Classifier (0) 2021.12.13 [기계학습] 1. Introduction to Machine Learning (0) 2021.12.12